
- #JEFFERSON FRACTURE FULL#
- #JEFFERSON FRACTURE CRACK#
The rib autograft is split with an oscillating saw and placed on either side of the O-C2 fusion site following arthrodesis via high-speed drill decortication. In this case, a rib autograft was harvested through a separate small 2-inch incision. An appropriate size rod is bent, cap screws are placed, and the construct is final tightened. Appropriate size/length screws are placed with optimally bicortical purchase. #JEFFERSON FRACTURE FULL#
The full length of the screw path is tapped to accommodate cortical screws. Drill guides are used in progressive 2-mm increments to drill the occipital keel, and a ball tip probe confirms when bicortical purchase has been achieved. A high-speed drill makes midline cortical entry points into the midline occipital keel. The Jefferson fracture classification system describes fractures of the atlas (first cervical vertebra or C1). The plate is bent to accommodate the contour of the occipital bone. An occipital plate is used for suboccipital fixation. 
#JEFFERSON FRACTURE CRACK#
lead pipe fracture one in which the bone cortex is slightly compressed and bulged on one side with a slight crack on the other side of the bone.
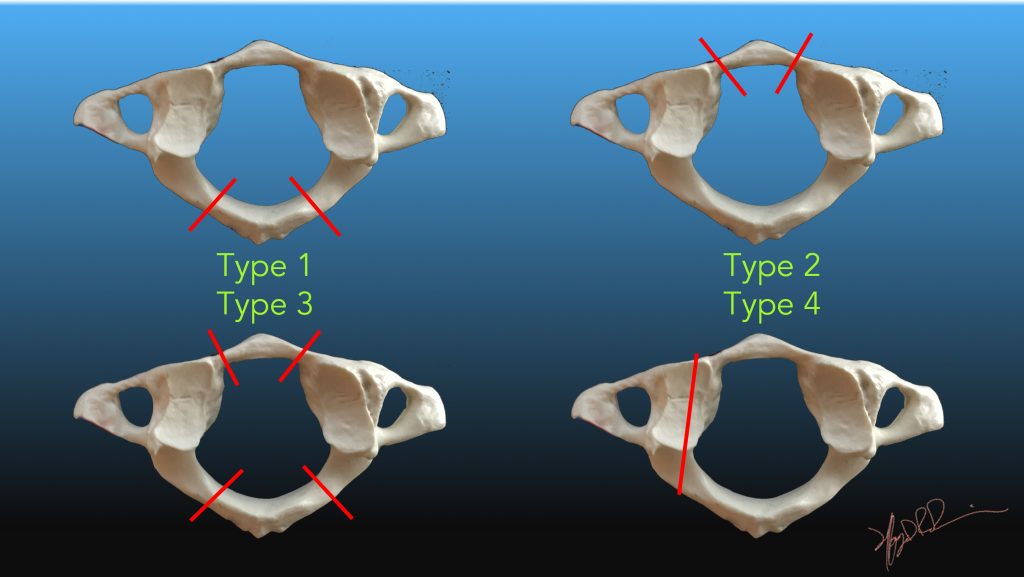
An undersized tap is used, followed by polyaxial screw placement (typical sizes 3.5-4.0 x 22-28 mm). Jefferson's fracture fracture of the atlas (first cervical vertebra). A Jefferson fracture may also cause damage to the arteries in. A ball tip probe is used to confirm that no breach has occurred. Patients with such fractures usually experience pain in the upper neck but no neurological signs. A hand drill is free-hand drilled down each lamina, guided by direct observation of the lamina contour. A high-speed drill is used to make cranio-caudally staggered cortical entry points into the spinous process of each side. C2-C3 facet joints and the C2-3 interspinous ligaments are left intact. "Evaluation and treatment of atlas burst fractures (Jefferson fractures)". ^ Kesterson L, Benzel E, Orrison W, Coleman J (1991). "James Platt White, MD (1811-1881): his interesting and remarkable accident". This fracture is caused by a compressive downward force that is transmitted evenly through the occipital condyles to the superior articular surfaces of the. "Treatment of stable burst fracture of the atlas (Jefferson fracture) with rigid cervical collar". ^ a b c Lee TT, Green BA, Petrin DR (1998). "Unstable Jefferson variant atlas fractures: an unrecognized cervical injury". "Atlantoaxial screw fixation for the treatment of isolated and combined unstable jefferson fractures - experiences with 8 patients". 
^ a b c d Hein C, Richter HP, Rath SA (2002)."Jefferson fracture in a child-illustrative case report". ^ a b Korinth MC, Kapser A, Weinzierl MR (2007)."Malformations of the atlas vertebra simulating the Jefferson fracture". ^ Gehweiler JA, Daffner RH, Roberts L (1983)."A congenital anomaly of the atlas as a diagnostic dilemma: a case report". "Fracture of the atlas vertebra: report of four cases, and a review of those previously recorded". Duke University Division of Orthopaedic Surgery. Conservative treatment with an immobilization device can produce excellent long-term recovery. Though a serious injury, the long-term consequences of a Jefferson's fracture are uncertain and may not impact longevity or abilities, even if untreated. A primary factor in deciding between surgical and non-surgical intervention is the degree of stability as well as the presence of damage to other cervical vertebrae. Surgical treatment of a Jefferson fracture involves fusion or fixation of the first three cervical vertebrae fusion may occur immediately, or later during treatment in cases where non-surgical interventions are unsuccessful. The use of rigid halos can lead to intracranial infections and are often uncomfortable for individuals wearing them, and may be replaced with a more flexible alternative depending on the stability of the injured bones, but treatment of a stable injury with a halo collar can result in a full recovery.
An intact ligament requires the use of a soft or hard collar, while a ruptured ligament may require traction, a halo or surgery. Non-surgical treatment varies depending on if the fracture is stable or unstable, defined by an intact or broken transverse ligament and degree of fracture of the anterior arch. Jefferson fracture is usually caused by axial impact to the head such as diving in. The use of surgery to treat a Jefferson fracture is somewhat controversial. S12.000A Unspecified displaced fracture of first cervical vertebra.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
